Interview
Software 2.0 AI for systems
data-centric AI
differentiable programming
Euclidean Space Hyperbolic Space
Combinatorial Optimization
RL+metrics classification + performance model?
Interpretability / Performance How to debug a model? Insight
https://towardsdatascience.com/what-is-feature-engineering-importance-and-techniques-for-machine-learning-2080b0269f10
Feature Engineering: Continuous features, categorical features, codes, one hots Missing Values, Duplicated values, Outliers Normalization (right normalization for model/problems), Scaling Modeling/Encoding Feature Split/Disentangle
Standardization: Standardization (also known as z-score normalisation) is the process of scaling values while accounting for standard deviation. If the standard deviation of features differs, the range of those features will likewise differ. The effect of outliers in the characteristics is reduced as a result. To arrive at a distribution with a 0 mean and 1 variance, all the data points are subtracted by their mean and the result divided by the distribution’s variance
Handling Outliers Outlier handling is a technique for removing outliers from a dataset. This method can be used on a variety of scales to produce a more accurate data representation. This has an impact on the model’s performance. Depending on the model, the effect could be large or minimal; for example, linear regression is particularly susceptible to outliers. This procedure should be completed prior to model training. The various methods of handling outliers include: 1. Removal: Outlier-containing entries are deleted from the distribution. However, if there are outliers across numerous variables, this strategy may result in a big chunk of the datasheet being missed. 2. Replacing values: Alternatively, the outliers could be handled as missing values and replaced with suitable imputation. 3. Capping: Using an arbitrary value or a value from a variable distribution to replace the maximum and minimum values. 4. Discretization : Discretization is the process of converting continuous variables, models, and functions into discrete ones. This is accomplished by constructing a series of continuous intervals (or bins) that span the range of our desired variable/model/function.
Log Transform Log Transform is the most used technique among data scientists. It’s mostly used to turn a skewed distribution into a normal or less-skewed distribution. We take the log of the values in a column and utilise those values as the column in this transform. It is used to handle confusing data, and the data becomes more approximative to normal applications.
Shapley Values (Game Theory) Mutual Information () PCA, LDA
AutoEncoder (unsupervised learning)
Monte Carlo Tree Search Thompson Sampling
model-free/model based RL
Markov Decision Process - S:环境的状态空间 - A:agent 可选择的动作空间 - R(s,a)R(s,a):奖励函数,返回的值表示在ss状态下执行aa动作的奖励 - T(s′|s,a)T(s′|s,a): 状态转移概率函数,表示从ss状态执行aa动作后环境转移至s′s′状态的概率
Storage Partitioning Advisor
- Feature Selection Methods
- Statistics for Filter Feature Selection Methods
- Numerical Input, Numerical Output
- Numerical Input, Categorical Output
- Categorical Input, Numerical Output
- Categorical Input, Categorical Output
- Tips and Tricks for Feature Selection
- Correlation Statistics
- Selection Method
- Transform Variables
- What Is the Best Method?
-
Worked Examples
- Regression Feature Selection
- Classification Feature Selection
-
Feature Selection: Select a subset of input features from the dataset.
- Unsupervised: Do not use the target variable (e.g. remove redundant variables).
- Correlation
- Supervised: Use the target variable (e.g. remove irrelevant variables).
- Wrapper: Search for well-performing subsets of features.
- RFE
- Filter: Select subsets of features based on their relationship with the target.
- Statistical Methods
- Feature Importance Methods
- Intrinsic: Algorithms that perform automatic feature selection during training.
- Decision Trees
- Wrapper: Search for well-performing subsets of features.
- Unsupervised: Do not use the target variable (e.g. remove redundant variables).
- Dimensionality Reduction: Project input data into a lower-dimensional feature space.

Feature Selection Filter Methods、Wrapper Methods、Embedded Methods Filter Methods 从训练数据的一般特征计算出某种度量,作为建模之前的处理步骤,为特征或特征子集评分。Filter Methods 通常要快得多,而且功能独立于学习算法,这意味着选择的特征可以传递到任何建模算法。Filter Methods 可以根据其使用的过滤措施,即信息、距离、依赖性、一致性、相似性和统计措施,进一步分类,例如 information gain,chi-square,Relief。
Wrapper Methods 使用任何独立的建模算法来训练使用候选特征子集的预测模型。通常用在一个固定的集合上的测试性能对特征集进行评分。另外,在随机森林中,可以根据估计的特征重要性分数来选择特征子集。在任何 Wrapper Methods 中,必须训练新模型来测试任何后续的特征子集,因此 Wrapper Methods 通常是计算密集的,但可以为特定建模算法识别最佳性能的特征集。Wrapper Methods 举例有向前向后等等。
Embedded Methods 将特征选择作为建模算法执行的一部分。这些方法的计算效率往往比 Wrapper Methods 更高,因为它们同时集成了建模和特征选择。例如,通过优化一个拟合优度项(Lasso, Elastic Net)对过多特征进行惩罚。与 Wrapper Methods 一样,Embedded Methods 选择的特征依赖于学习算法。Embedded Methods 举例有 Lasso, Elastic Net,以及各种基于决策树的算法,例如 CART, C4.5,以及 XGBoost。
Wrapper Methods 或 Embedded Methods 的一个优点是,通过子集评估,它们可以捕获特征依赖,或者说特征的相互作用。相比之下,很少有 Filter Methods 声称能够处理交互项。Relief 算法及其延伸的一系列算法,据我所知,是唯一能够检测特征依赖的单个 Filter Methods。Relief 算法使用最近邻概念来获得特征统计数据,从而间接地解释相互作用。此外,Relief 算法及其延伸的一系列算法相对较快。
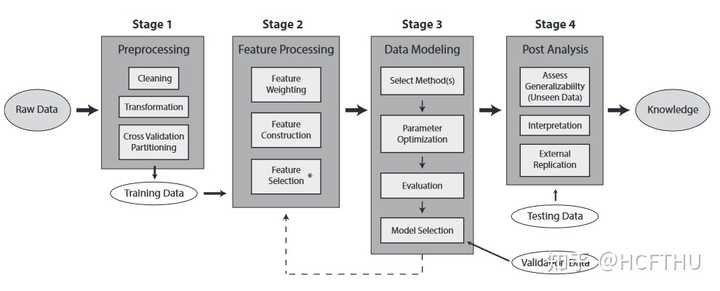
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1711.08421v2.pdf
作者:林德博格
链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/19774445/answer/1864178188
来源:知乎
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
1)我们的算法是属于哪一类?
- Supervised(classification、regression)、
- unsupervised(clustering)、
- semi-supervised.
2) 我们的特征空间属于哪一类:
- Flat features (也就是我们最常见的Dataset的情况,特征是静态的、而且彼此之间不存在特定的组织架构关系,结合后面两点对比来看就能理解);
- Structured Features(特征之间存在一定的组织架构关系),比如说 Group Structure(某些特征属于特定小组,若选则全都选、若不选则全都不要) 、Tree Structure (特征之间存在父子包含关系,若父特征被选中,则所有的子特征都会被选中)
- Streaming features (随着时间的变动,会采集新的特征)
3)最后才是考虑你喜欢哪一种Feature Selection方法:
- Filter方法: 这类方法将从Dataset的feature本身出发,考察变量之间的相关性(correlation)等,并不考虑做了feature selection之后你使用的特定算法。举个例子:如果说数据是有label的(我们的算法是classification),并且我们的特征空间是flat feature,那么它可能会计算label和其它feature之间的相关性来找到relevant features; 然后再考察relevant features之间的相关性,来找到redundant features. 如果我们的数据是没有label(我们的算法是clustering)那么可能直接计算features之间的相关性,或者使用其它方法。这类方法其实是最基本的,但是在国内的统计学教科书上很少做相关介绍。比如说,我们可以使用Fisher score, Mutual Information , Relief 等来衡量上述的correlation.
- Wrapper方法:这类方法在做feature selection的时候,先选出来一部分特征,然后将这部分特征用于运行你的特定算法(比如说决策树),看看表现如何;然后重复上述步骤,直到选出“最好的”特征子集为止。
- Embedding 方法:这一类方法的话,就是把feature selection这种思想在算法里built-in了,并不单独拎出来。举个例子:见下图,就lasso回归来说,在拟合误差项后面再给你整一项惩罚项来进行feature selection。
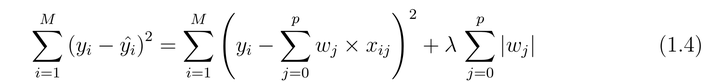
我们可以看到这就是built-in的思想,你无法将其单拎出来,而是“浑然天成“一体。再说一点题外话,在实际应用中,如果feature dimension过于庞大,一般都是使用filter方法;或者是使用filter方法进行预处理,剔除一批“劣质”特征,然后再使用Wrapper或者Embedding进行“精选”。